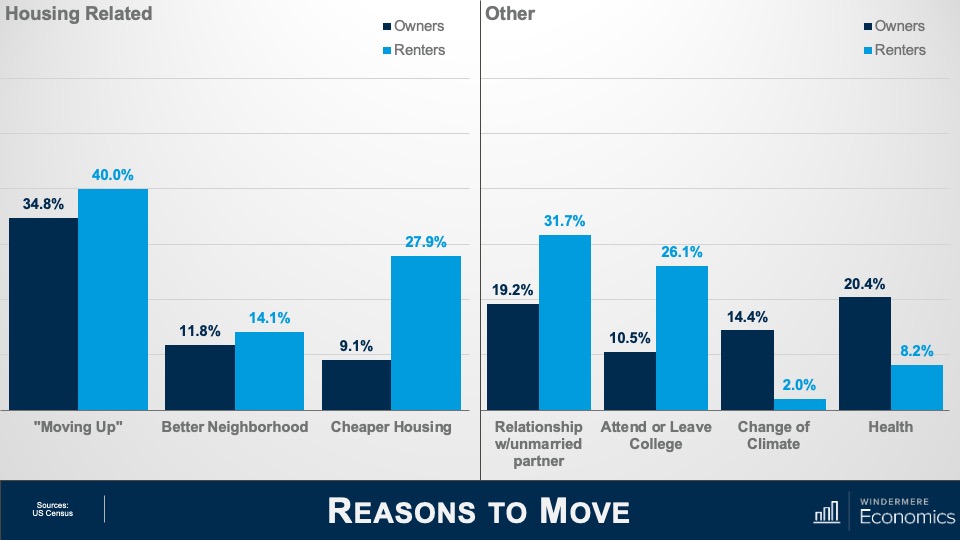
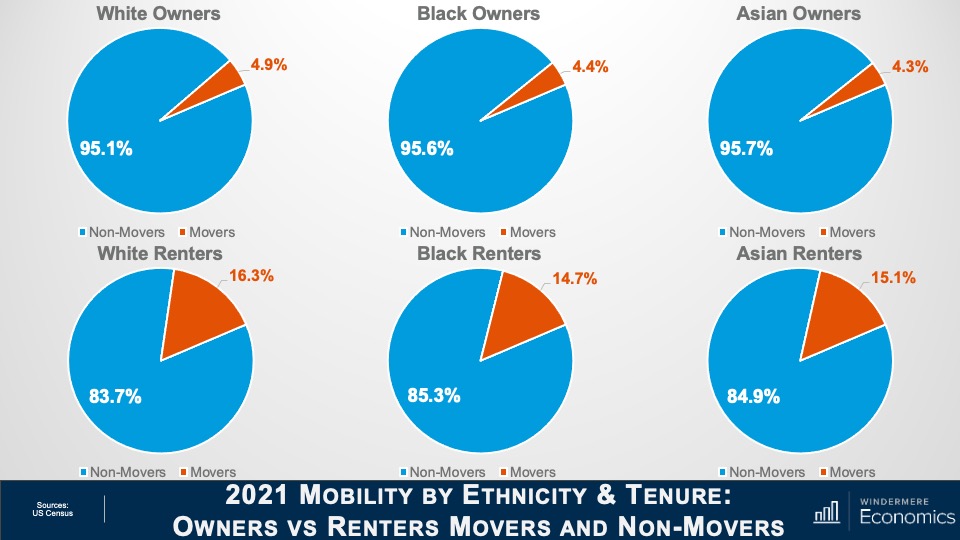
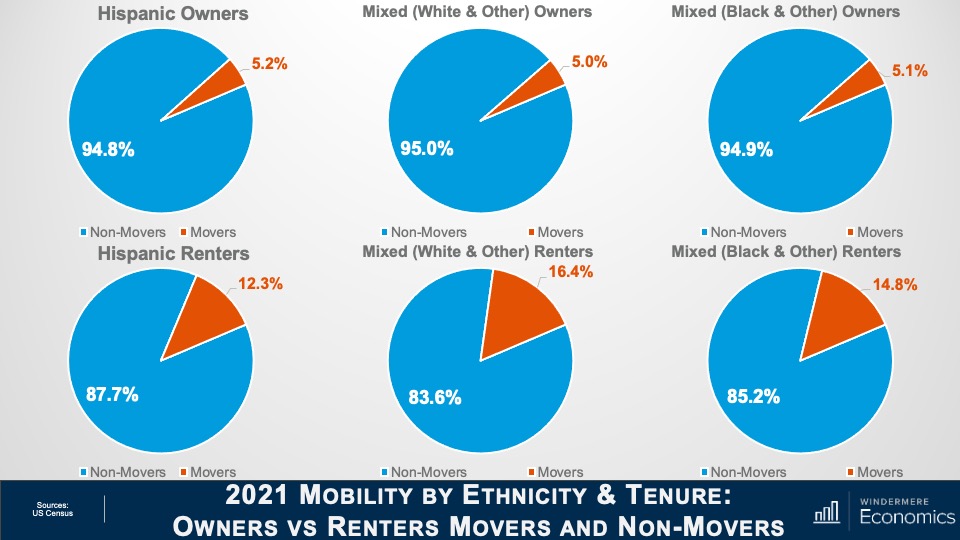
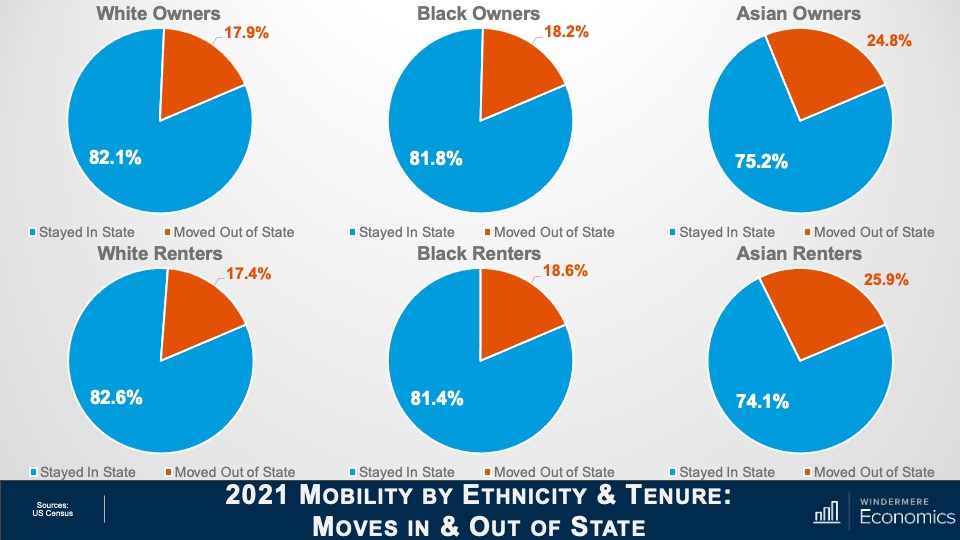
How will rising foreclosures impact the U.S. housing market? To give his answer, Windermere Chief Economist Matthew Gardner sheds light on the latest foreclosure data and shows how prepared home buyers are to manage their mortgage debt today compared to the 2000s.
This video on foreclosures is the latest in our Monday with Matthew series with Windermere Chief Economist Matthew Gardner. Each month, he analyzes the most up-to-date U.S. housing data to keep you well-informed about what’s going on in the real estate market.
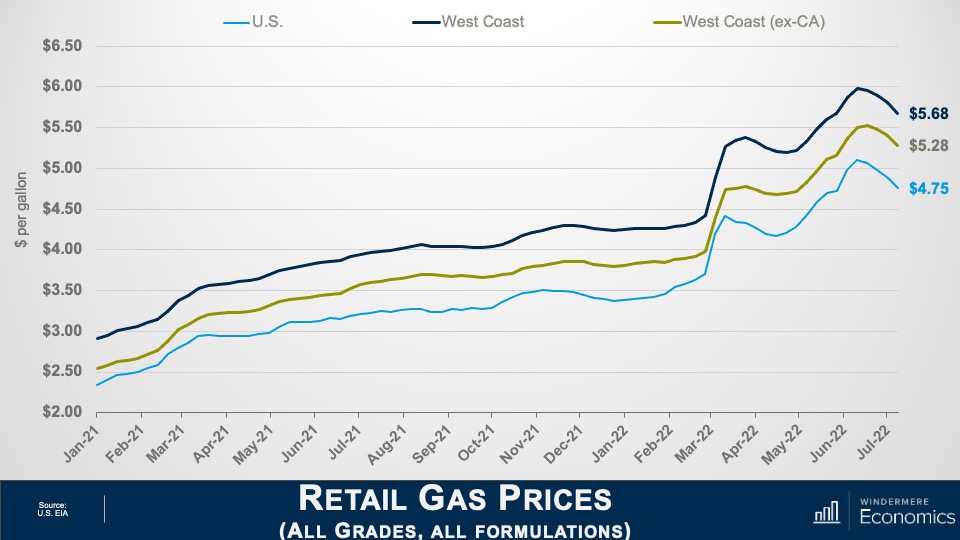
Rising U.S. Foreclosures
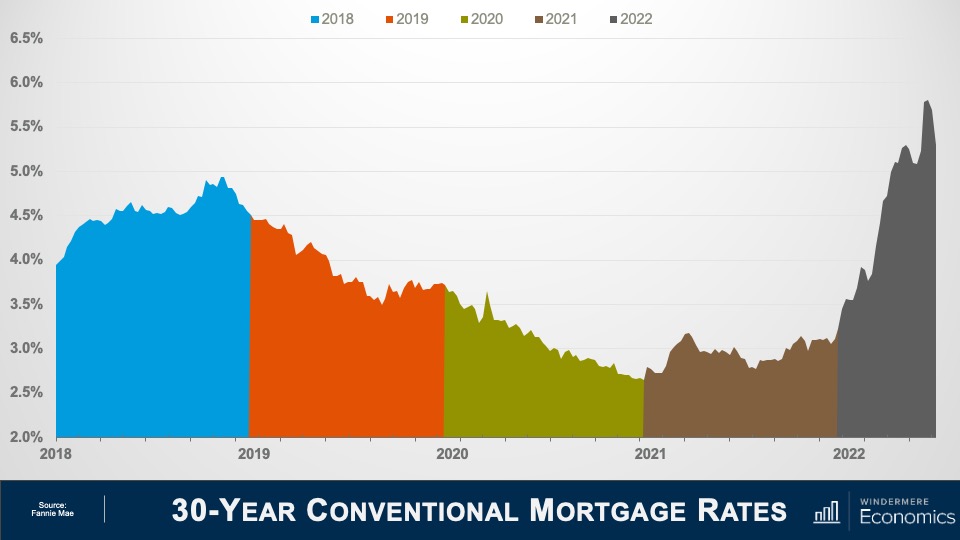
The market has certainly shifted since mortgage rates started skyrocketing last year and, with prices pulling back across much of the country, some have started to become concerned about the likelihood of foreclosures rising—clearly a timely topic given current circumstances.
Hello there! I’m Windermere Real Estate’s Chief Economist Matthew Gardner and for this month’s episode of Monday with Matthew, I pulled the latest data on foreclosure starts and looked and the quality of mortgages that have been given to buyers in order to give you a clear idea of how foreclosures will impact the overall housing market.
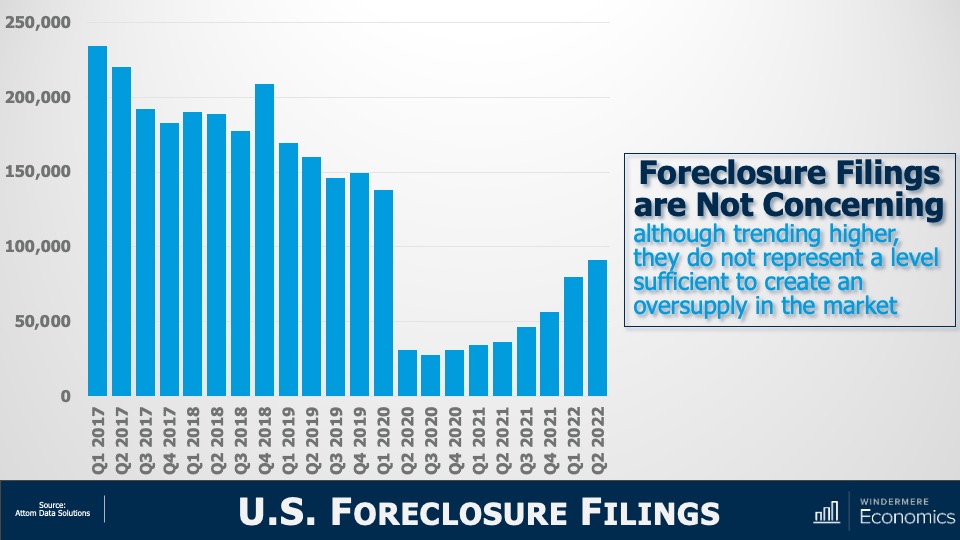
For the purposes of this exercise, I’m going to concentrate on foreclosure starts rather than foreclosure filings because data shows us that a majority of homeowners where a foreclosure filing has been submitted to a court by their lender are able to avoid it by refinancing or selling the home, which makes total sense as over 93% of owners in the U.S. have positive equity.
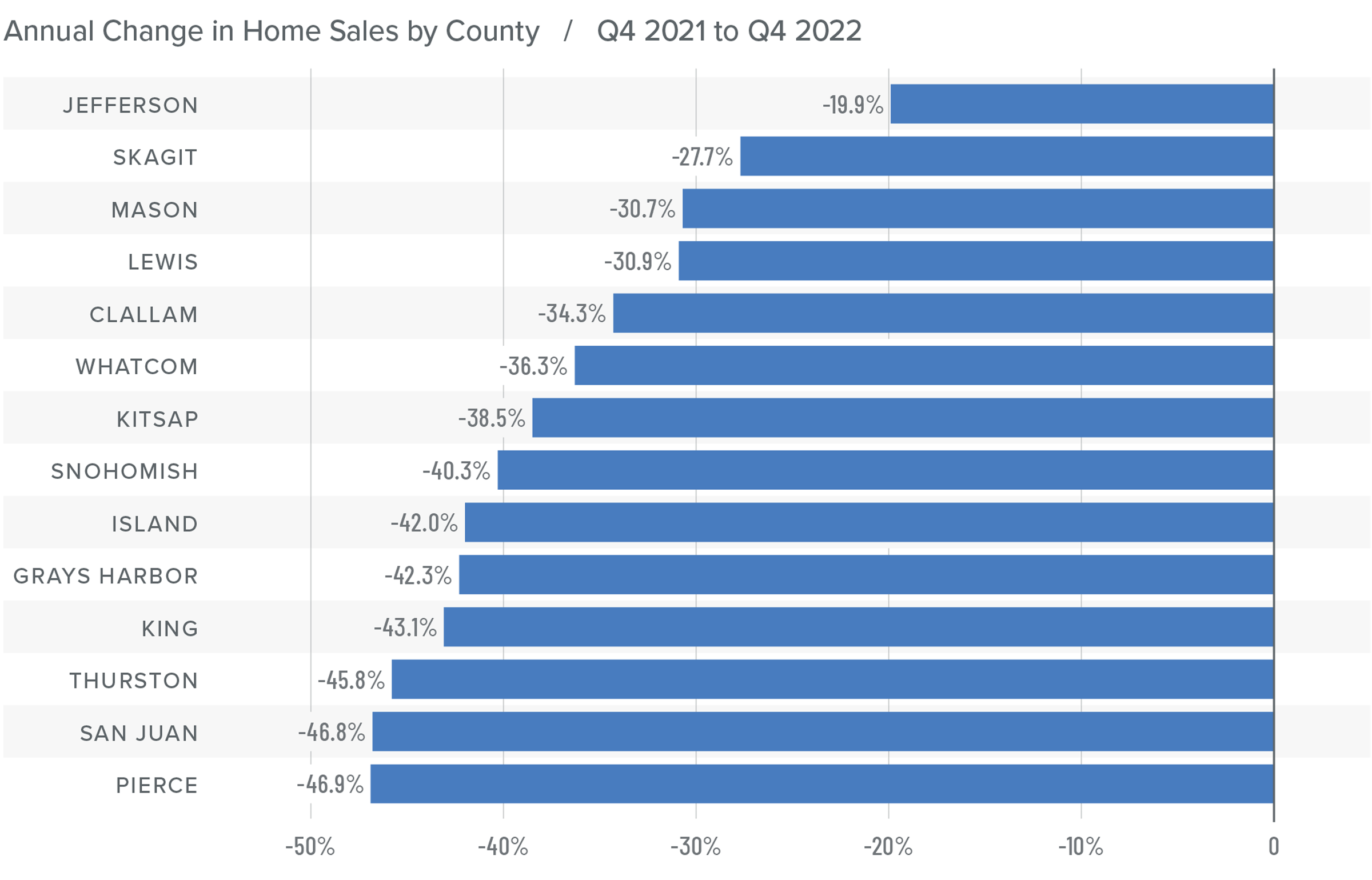
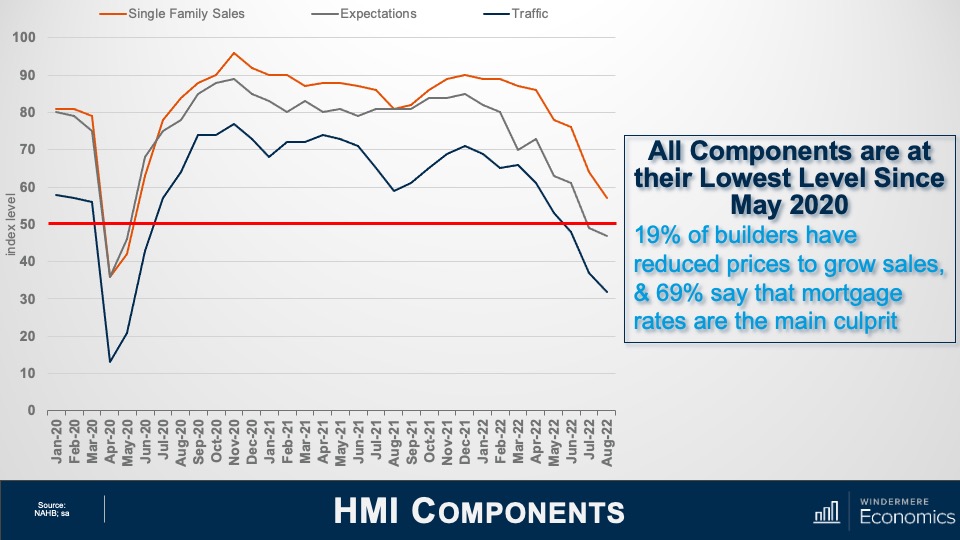
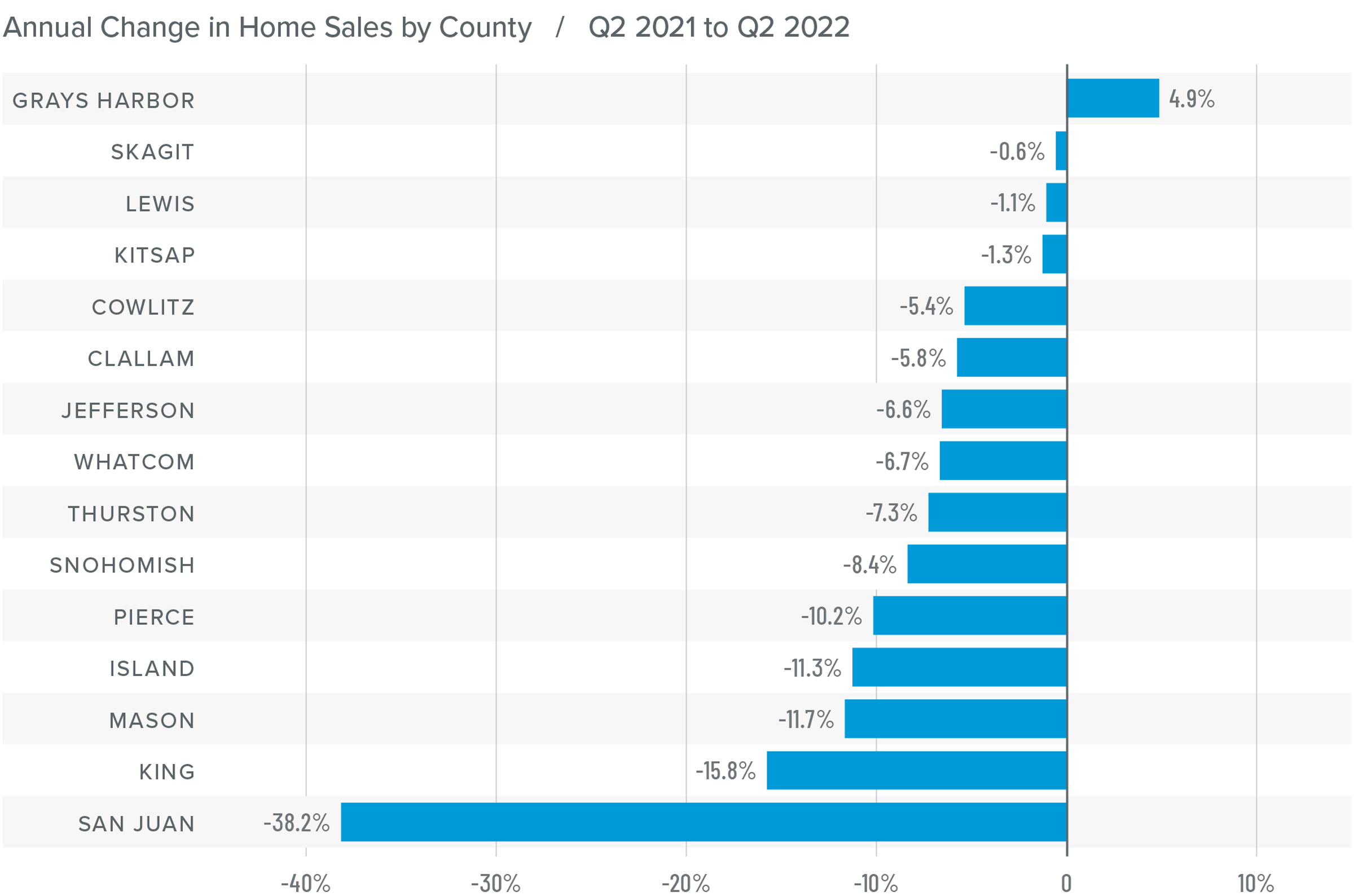
U.S. Foreclosures: Starts 2007-2022
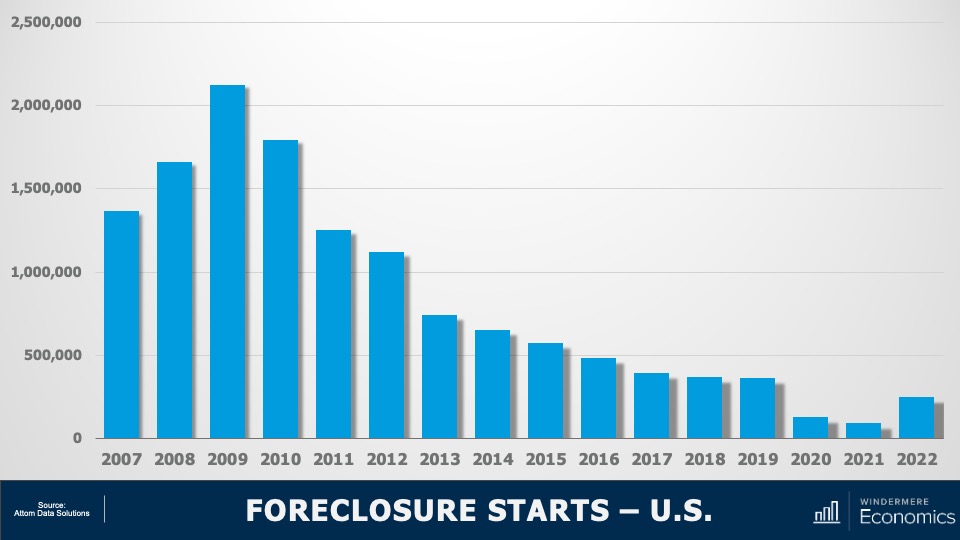
As you can see here, foreclosure starts rose significantly last year. In fact, they were 181% higher than in 2021. But if we zoom out, it’s important to note that foreclosure starts were 31% lower than 2019 and 88% lower than the 2009 peak.
Am I surprised at the increase in foreclosure starts? Not really. The forbearance program was put in place at the start of the pandemic, and it allowed homeowners to temporarily stop making mortgage payments and not be foreclosed on, but that program ended 18 months ago.
And, although a vast majority of the 4.7 million households who entered the program have left it and sold or refinanced their homes, there were always going to be some who were not able to, and this has led to the overall foreclosure activity rising. Let’s take a closer look.
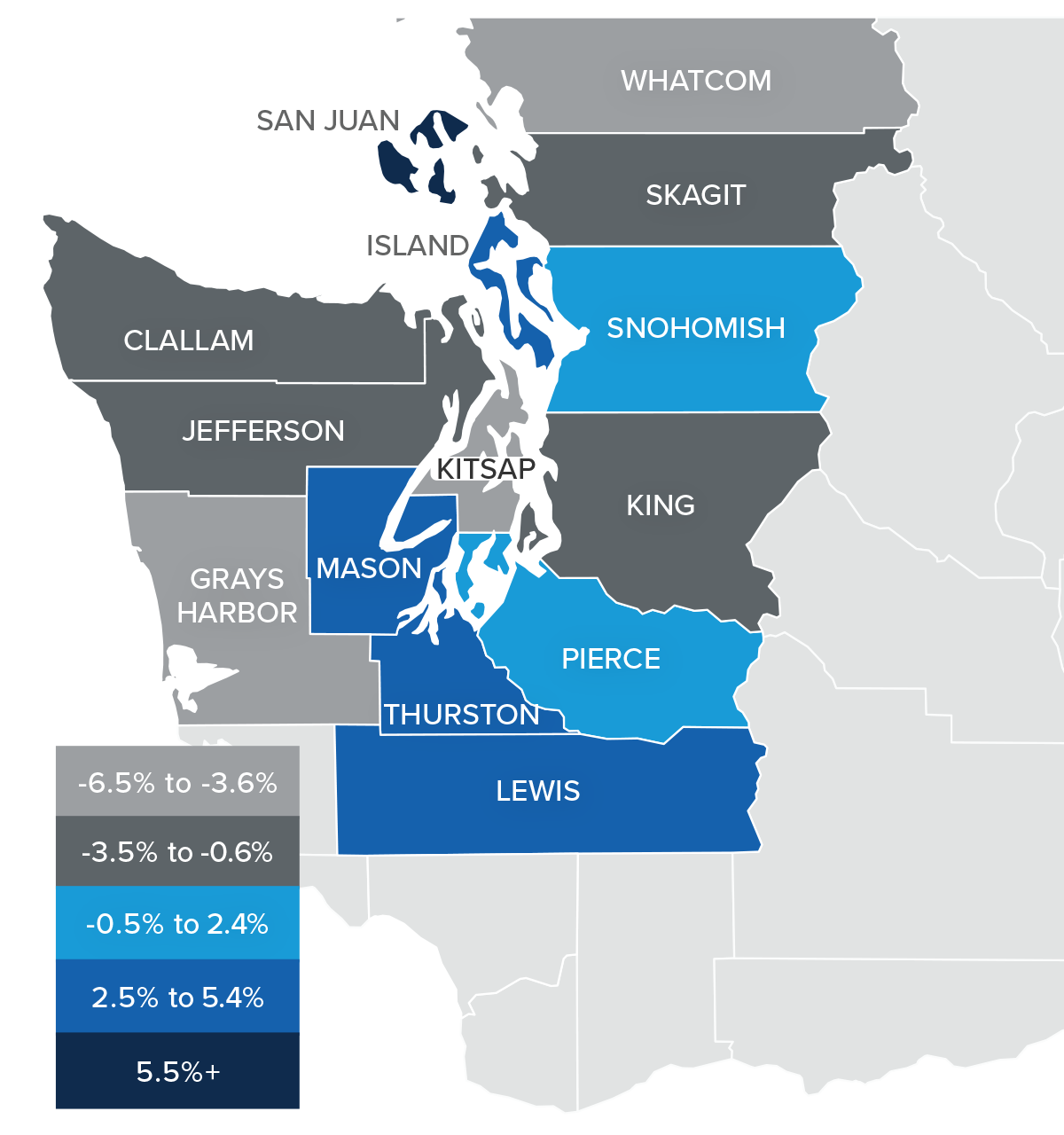
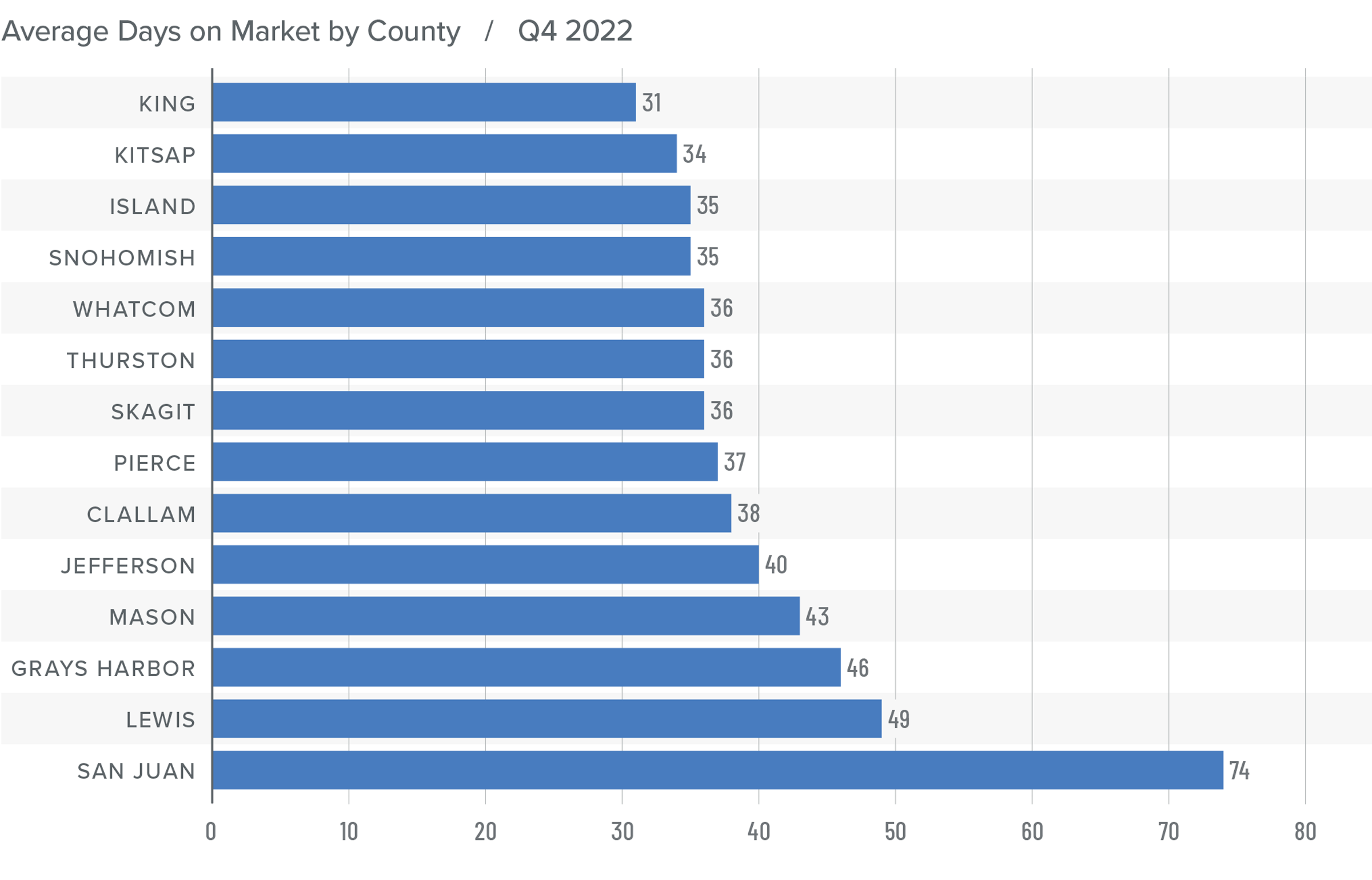
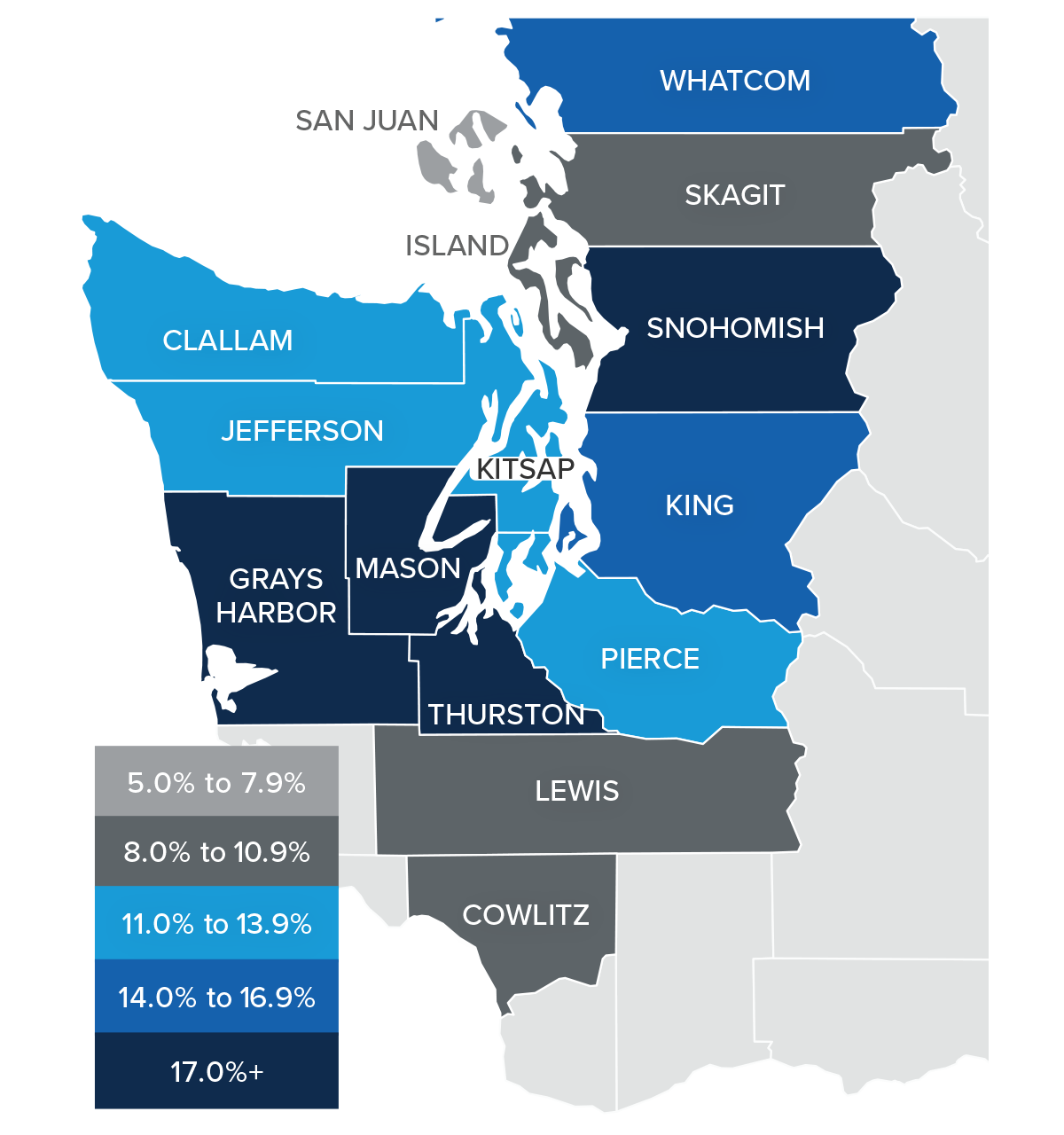
U.S. Foreclosures in 2022
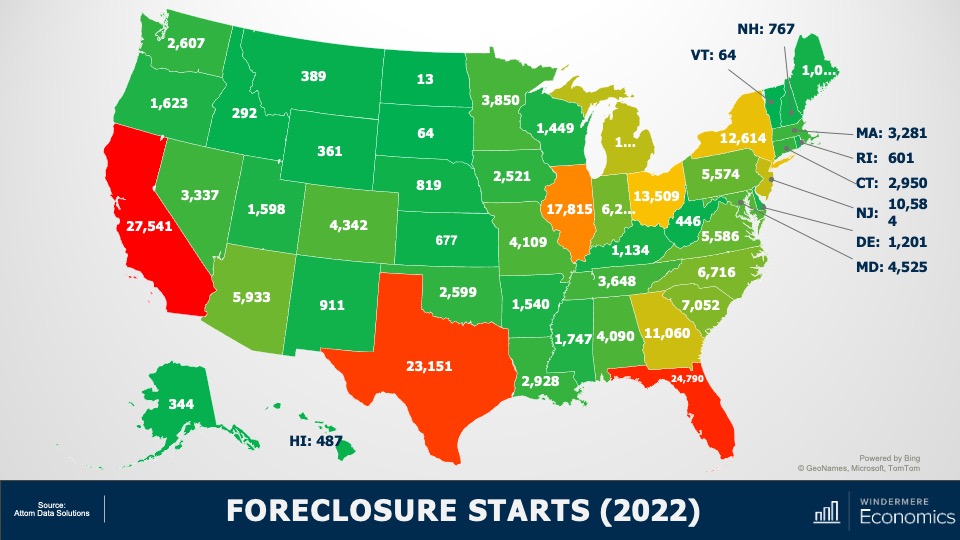
This is a heat map of foreclosure starts by state. And you can see that California, Florida, and Texas saw the highest numbers in 2022. But remember that these are the states that have the greatest number of homes with mortgages so, statistically, we would expect the total number of homes in foreclosure in those states would be higher than the rest of the country. That said, foreclosure starts were significantly higher in Florida, California, Texas, and New York than they were in 2019, the last “pre-COVID” year and before the forbearance program started.
And when we look more myopically, metro areas including New York/New Jersey, Washington DC, the Delaware Valley, Atlanta, Miami, Baltimore, and Dallas all saw total foreclosure starts rise well above what they were in 2019. This may suggest that there are some markets that could see foreclosure activity rise to a level that could materially impact housing in those locations.
But looking at the country as a whole, there are other factors leading me to believe that we will not see the number of homes entering foreclosure rising above the long-term average, and certainly not sufficient to have a material impact on U.S. housing prices.
Let me show you what’s happening on the mortgage side of things. First: credit quality.
Median FICO Scores for New Mortgages 2003-2022
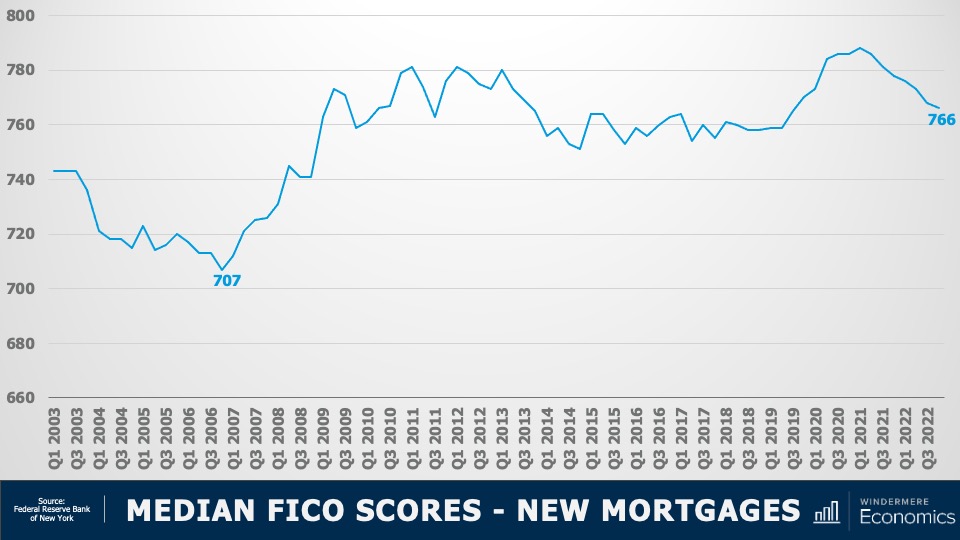
The median FICO score for new mortgages was 766 in the 4th quarter of 2022. Yes, this is down from the peak seen in early 2021 when it was a whopping 788 but as shown here, it’s far higher than we saw before the housing crisis. Buyers over the past several years had very good credit and, given the tight labor market, we are certainly in a very different place than back before the housing bubble burst.
Mortgage Debt Payments Percentages 2007-2022
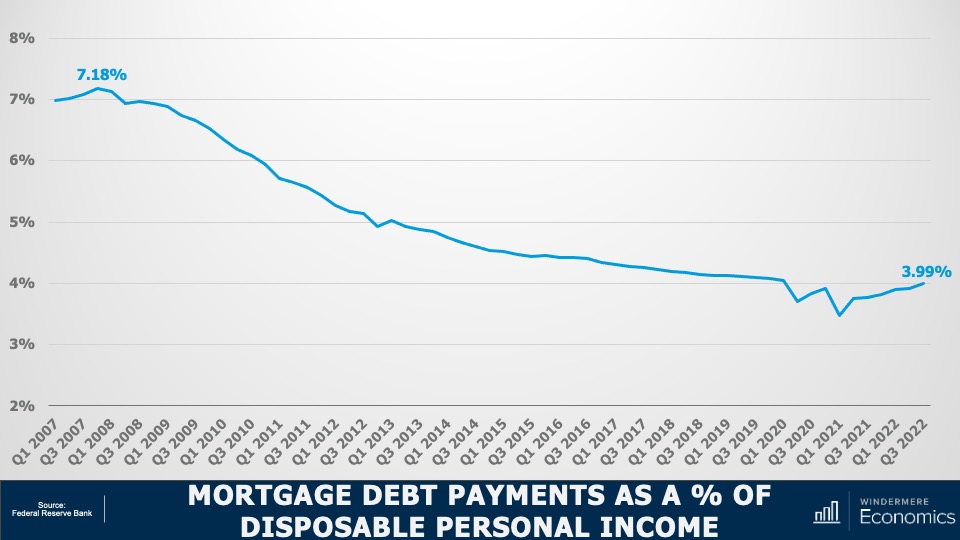
Secondly, buyers are using larger down payments than in the mid-2000’s, and with the historically low mortgage rates that we saw during the first two years of the pandemic benefitting new buyers as well as allowing existing homeowners to refinance, the share of disposable income that is used to cover mortgage payments remains very low. This basically means that owners aren’t as burdened by their house payments as they were in 2007-2009. And finally…
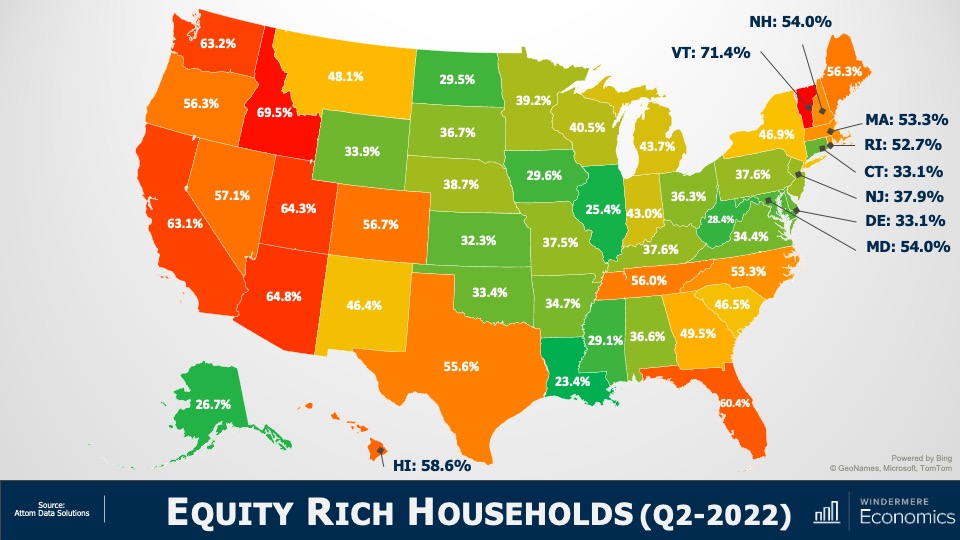
Equity Rich Households Q4 2022
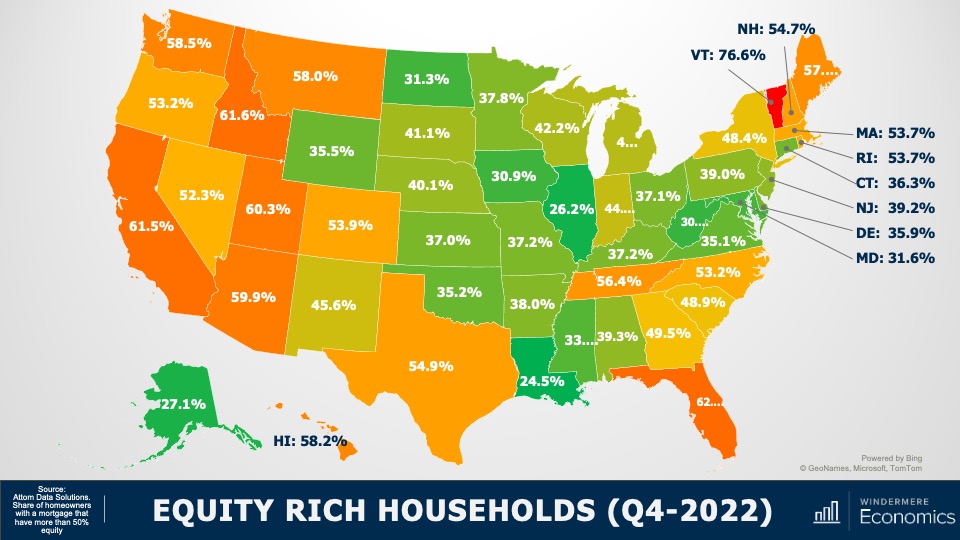
With the significant run-up in housing values that we have seen over the past few years, 48% of all homeowners with a mortgage have more than 50% equity. Although this share has pulled back a little as mortgage rates rose and values pulled back, it’s still a massive amount of money and, as I mentioned earlier, many homeowners who are faced with foreclosure will end up selling their homes as they still have positive equity rather than go through the foreclosure process.
So, my answer to those of you wondering if we will see foreclosures rise to a level that could impact the overall housing market is “no.”
I don’t see any reason to believe that distressed sales will hurt the market in general, but I will say that there are some local markets where distressed sales could rise to levels that could act as a headwind to price growth in these areas. As always, I’d love to get your thoughts on this topic so please comment below! Until next month, take care and I will see you all soon. Bye now.
To see the latest housing data for your area, visit our quarterly Market Updates page.
About Matthew Gardner
As Chief Economist for Windermere Real Estate, Matthew Gardner is responsible for analyzing and interpreting economic data and its impact on the real estate market on both a local and national level. Matthew has over 30 years of professional experience both in the U.S. and U.K.
In addition to his day-to-day responsibilities, Matthew sits on the Washington State Governors Council of Economic Advisors; chairs the Board of Trustees at the Washington Center for Real Estate Research at the University of Washington; and is an Advisory Board Member at the Runstad Center for Real Estate Studies at the University of Washington where he also lectures in real estate economics.